Scaling Your Startup with No-Code AI Automations: A Step-by-Step Guide
Scaling Your Startup with No-Code AI Automations: A Step-By-Step Guide
Meta Description: Scaling your startup with no-code AI automations can unlock rapid growth without a single line of code. Discover this step-by-step guide to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and drive sustainable expansion for your business.
Outline:
- Introduction – Overview of scaling challenges and how no-code AI automations serve as a step-by-step solution for startup growth.
- Understanding No-Code AI Automation – Definition of no-code platforms and AI automation, and how their convergence empowers non-technical founders.
- Why Automations Are Key to Scaling – Explanation of why automating processes is crucial for growing startups (time savings, consistency, cost efficiency).
- Benefits of No-Code AI for Startups – Specific advantages (speed, cost savings, error reduction, productivity, scalability) of using no-code AI tools in a startup.
- Identifying Automation Opportunities – How to pinpoint repetitive tasks and bottlenecks in various departments (marketing, sales, customer support, operations) that are ripe for automation.
- Setting Clear Automation Goals – Importance of defining objectives and metrics (e.g., reduce response time by 50%, handle 2x customers) before implementing automation.
- Step 1: Map Out Repetitive Tasks – Step-by-step guide begins with auditing daily workflows to list tasks that consume time and are prone to human error.
- Step 2: Choose the Right No-Code Tools – Guidance on selecting no-code platforms (workflow automation tools, app builders, AI services) best suited to your startup’s needs, with examples like Zapier, Bubble, or Airtable.
- Step 3: Build Your First Automation – Start small by automating a single process (e.g., lead notification, email response) to demonstrate value and learn the ropes.
- Step 4: Integrate AI for Advanced Tasks – Incorporating AI capabilities (such as chatbots for customer service or AI analytics for decision-making) once basic automation is in place.
- Step 5: Streamline and Document Processes – Refining workflows to integrate automations smoothly, documenting new processes, and training team members to use AI tools effectively.
- Step 6: Monitor, Measure, and Iterate – Tracking performance metrics (time saved, error rates, customer satisfaction) and continuously improving the automation workflows.
- Step 7: Scale Up Your Automations – Expanding automation to more areas of the business and handling increased volume without additional headcount.
- Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success – Addressing common concerns (tool limitations, when to involve developers, data security) and tips for successful adoption (getting team buy-in, avoiding over-automation).
- Popular No-Code AI Tools for Startups – A brief overview of notable no-code AI platforms and tools across different categories (integration, app-building, chatbots, analytics) that can facilitate scaling.
- FAQs – Answers to common questions about no-code AI automations in startups (e.g., what it is, ease of use, cost, security, etc.).
- Conclusion – Recap of key points, encouragement to leverage no-code AI for growth, and final optimistic take on scaling efficiently as a founder.
Introduction
Scaling a startup is both an exciting and challenging endeavor. As your user base grows and operations become more complex, maintaining efficiency and quality can feel like a high-wire act. Scaling your startup with no-code AI automations offers a step-by-step solution to this challenge, allowing you to grow faster without proportional increases in cost or workload. Instead of scrambling to hire more staff for every new project or firefighting operational bottlenecks, founders can leverage no-code tools and artificial intelligence (AI)—the simulation of human intelligence by machines, which enables automation of tasks, data analysis, and decision-making in business operations—to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows. This step-by-step guide will walk you through how to harness no-code AI automations to supercharge your startup’s growth, all while keeping things simple and code-free.
In the early stages of a startup, team members often wear many hats, juggling everything from customer support to marketing. It’s easy for small teams to become overwhelmed as the business gains traction. Fortunately, we live in an age where you can offload a lot of that busywork to no-code automation platforms and smart AI tools. These solutions are helping non-technical founders and teams understand, implement, and benefit from automation, making it easier to streamline operations and drive business growth. Picture having a digital workforce handling routine emails, data entry, customer inquiries, and even generating reports – leaving you and your team free to focus on strategic, creative, and high-value activities. Not only does this boost productivity, but it also ensures that critical processes run consistently every time, which is key to delivering quality at scale.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand what no-code AI automation is and why it’s a game-changer for modern startups looking to scale up. We’ll dive into specific steps – from identifying what to automate, to choosing the right tools, implementing your first automated workflow, and integrating AI for even more powerful capabilities. Along the way, we’ll highlight real-world examples, best practices, and common pitfalls to avoid. Whether you’re a non-technical founder or simply looking to do more with less, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take your startup to the next level using no-code AI automations. Let’s get started on the journey to effortless growth!
Understanding No-Code AI Automation
Before jumping into the how, let’s clarify what we mean by no-code AI automation. No-code development platforms are tools that allow entrepreneurs and teams to build software applications or set up workflows without writing a single line of code. Instead of traditional programming, you use intuitive graphical interfaces – think drag-and-drop components, visual workflow builders, and pre-built integrations – to create apps or automated processes. No-Code AI platforms often include pre-built templates and guided workflows to facilitate successful application creation. This means someone with no formal coding experience can create a functional application or automation script, which historically would have required a software developer. No-code platforms range from website and app builders (like Webflow or Bubble) to workflow automation services (like Zapier or Make) that connect different apps together.
Now, add artificial intelligence into the mix. AI automation refers to using AI-powered tools to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence – such as understanding natural language, analyzing data, making decisions, or recognizing patterns – all without constant human intervention. When we talk about no-code AI automation, we’re looking at platforms or solutions that let you incorporate AI capabilities into your processes without having to code or build the AI from scratch. In practical terms, this could be as simple as using an AI-driven chatbot that you can set up with a visual interface, or an AI service that analyzes your sales data and gives predictions via a no-code dashboard. Essentially, no-code AI automation enables you to design and deploy AI-driven processes through point-and-click tools and plain language instructions rather than complex programming.
For example, imagine you want a system that sorts customer support emails and sends personalized replies. In the past, building such an AI system would require machine learning experts and lots of code. Today, a no-code AI tool can let you set this up by selecting pre-made AI models (for text analysis or sentiment detection) and drawing a simple workflow: “If email contains X, respond with Y.” The AI handles the heavy lifting (understanding the email’s intent and choosing the right response), while the no-code interface lets you control the logic without coding. This convergence of no-code and AI is empowering non-technical founders to implement sophisticated solutions that were once out of reach. According to industry research, the global no-code platform market is projected to grow at a remarkable 24.1% CAGR through 2031, underscoring how integral these tools are becoming for businesses of all sizes. In short, no-code AI automation democratizes technology, allowing startups to leverage cutting-edge AI and automation techniques without needing a full engineering team.
Why Automations Are Key to Scaling
Scaling a startup means handling more customers, more data, and more complexity – often with the same small team and limited budget you started with. Automation becomes your secret weapon to do more with less. By automating routine and repetitive tasks, you ensure that operations can expand in volume and scope without a corresponding spike in manual workload or errors. Automating repetitive tasks enhances workflow efficiency, accelerates product development, and is pivotal for scaling startups by allowing teams to achieve more with fewer resources. In other words, automation lets you increase output and efficiency in a way that linear hiring cannot. This is crucial for startups, where resources are tight and speed is of the essence.
An upward-trending graph symbolizes how leveraging automation can drive startup growth by improving efficiency and output.
When you automate processes, you achieve consistency and reliability at scale. For instance, if you have an onboarding process that every new user goes through, automating it (via triggered emails, in-app tutorials, etc.) means whether you have 100 users or 100,000 users, each one gets the same thorough experience without overwhelming your team. Automation also dramatically cuts down the time required to accomplish tasks. What might take an employee hours of clicking, copying, and pasting can be done by a well-set-up automation in seconds. The cumulative time savings allow your team to focus on innovation, strategy, and customer engagement – the things that truly drive growth. As Zapier, a leader in the automation space, points out, by automating large-scale processes you can “get a lot more done without needing to add additional headcount” to your team.
Another reason automations are key to scaling is error reduction. Humans, especially when stretched thin, can make mistakes – miss an email, enter a wrong number in a spreadsheet, etc. Automated workflows perform tasks the same way every time, according to the rules you set, virtually eliminating certain types of errors. This improves quality and reliability of your service as you grow. Automation also provides speed and agility. Startups often need to adapt quickly; an automated system can be changed or scaled instantly (e.g., updating a workflow in your no-code tool affects all future transactions immediately), whereas managing a larger team or manual process can be like turning a ship.
Crucially, automation isn’t just about internal efficiency – it directly impacts customer experience. For example, faster response times due to automated customer support, or personalized marketing campaigns triggered by AI, can significantly boost customer satisfaction and conversion rates. In a Harvard Business Review analysis, business leaders affirmed that automation is now a “must-have” to improve not only productivity but also to deliver better customer and employee experiences at scale. All these factors make automation an engine for scalable growth: it multiplies your efforts without multiplying your costs.
Benefits of No-Code AI for Startups
Adopting no-code AI automation in your startup brings a host of benefits that directly contribute to scalability and success. Let’s highlight some key advantages:
- Rapid Development and Deployment: No-code tools drastically shorten the development cycle. You can build a prototype or set up a new automated workflow in days or weeks instead of months. This speed of development means you can iterate quickly, test ideas faster, and respond to market opportunities or challenges in real time. For instance, entrepreneurs can create a minimum viable product (MVP) via a no-code platform in a fraction of the time it once took. Faster iterations lead to a shorter time-to-market, which is invaluable for staying competitive and capturing early customers.
- Low Cost and Resource Efficiency: Traditional scaling often meant hiring more people or investing heavily in software development. No-code AI automation flips that script. Many no-code platforms are affordable (some even have free tiers to start), and implementing automation can save the cost of additional hires. Hiring developers and managing infrastructure is expensive, with one software engineer costing over $120,000 yearly in the U.S. By automating tasks without coding, startups reduce the need to bring in expensive developers for every new feature or process improvement. You’re effectively doing more with the team you have. Furthermore, automation can cut operational costs by reducing errors and improving efficiency – less money is lost to mistakes or delays, and more value is created per employee.
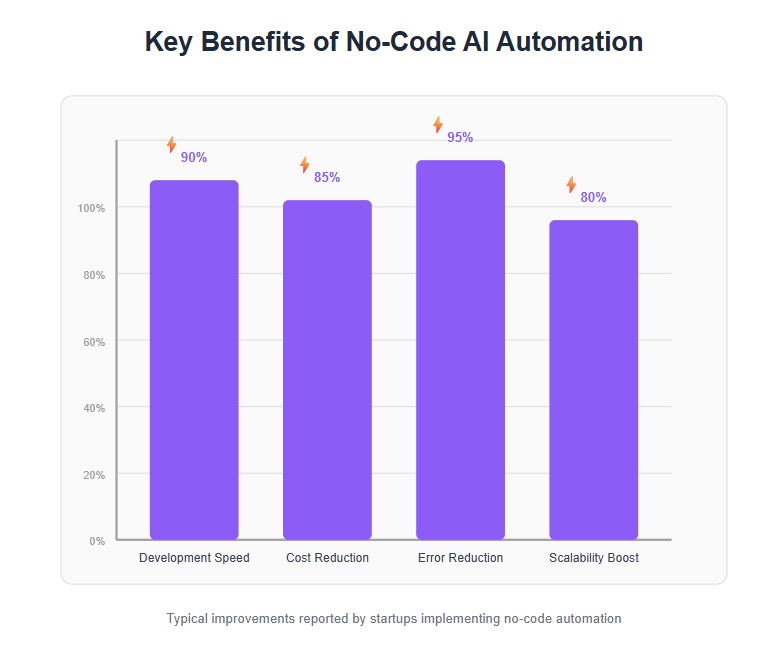
In summary, no-code AI automation gives startups speed, efficiency, and agility – exactly what a young company needs to punch above its weight. By leveraging these benefits, you position your startup to handle growth gracefully, turning potential growing pains into competitive advantages.
Identifying Automation Opportunities
Knowing the why of automation is great, but where do you start? The first step is to identify what tasks or processes in your startup should be automated. Not everything is a good candidate for automation – you want to target repetitive, time-consuming tasks that don’t require deep human insight, as well as processes prone to error or delay. Here’s how to uncover those opportunities:
Begin by observing and listing your routine daily and weekly operations. Which tasks are done over and over in the same or similar way? Common culprits are data entry (e.g. copying info from one system to another), report generation, sending out standard emails (welcome emails, follow-ups, reminders), social media posting schedules, and so on. For each team or function in your startup, brainstorm what consumes their time needlessly. For example, in customer support, are your team members manually answering the same FAQs via email or chat? In marketing, perhaps they spend hours every week exporting and cleaning data to analyze campaign results. In sales, maybe leads from your website form are being manually compiled and assigned. These are strong candidates for automation.
Also consider points of friction or bottlenecks. Ask yourself: Where do delays happen in our workflow? Is there a step where work sits idle waiting for someone to take action? Often, automations can be introduced to trigger immediate actions so nothing falls through the cracks. For instance, if leads are not promptly followed up on because the sales rep isn’t notified in time, an automation can instantly alert the team or even respond on its own. Look for any “copy-paste” work your team does – moving data between spreadsheets and systems is a prime example that tools like Zapier or Make can handle seamlessly by integrating those systems.
Another area to examine is multi-step processes with clear rules. Workflow automations shine when you have an “if X happens, do Y” scenario. For example: if a customer submits a support ticket, then log it in a database, send an acknowledgment email, and notify a Slack channel. If you find yourself describing a process in such conditional steps, chances are it can be automated end-to-end. Modern automation platforms allow you to chain together a series of actions across different apps easily, so take a holistic view of your processes.
Don’t forget to solicit input from your team. The people doing the work often know exactly what tasks are menial or frustrating. They can tell you, “I spend half my day doing X, which is basically the same steps each time.” Those pain points are golden opportunities to apply no-code solutions. Encourage a mindset of “automate anything that doesn’t require creative human judgment.” As one solopreneur principle states, never let a human be your point of failure for routine work – if a task can be automated or delegated to a machine, it probably should be. This doesn’t diminish human value; rather, it frees your team to concentrate on areas where human touch and creativity make the difference, like strategy, relationship-building, and innovation.
To systematically identify opportunities, it can help to break it down by department or function:
- Marketing: Look at content scheduling, social media posting, email marketing campaigns, lead nurturing sequences, and analytics reporting. Many of these can be automated. For example, content marketing can be aided by AI tools that generate social posts or even draft blog outlines, and scheduling tools can auto-post across platforms.
- Sales: Consider lead management and follow-ups. Automatically qualify leads with a questionnaire, log interactions in the CRM, and send follow-up emails or reminders without manual intervention. There are no-code sales automation tools that can do things like move deals through pipeline stages or trigger actions when a deal is won/lost.
- Customer Support: Frequently asked questions can be handled by an AI-driven chatbot 24/7. Ticket routing and status updates can be automated so customers aren’t left waiting. For instance, startups commonly deploy no-code chatbots on their website that answer questions or create support tickets for a human agent if needed. AI chatbots can handle multiple inquiries at once, dramatically reducing wait times for customers.
- Operations/Finance: Think of automating invoice processing, data backups, or inventory alerts. If you have an e-commerce element, things like sending restock orders or low-inventory alerts can be automated. Internal reminders (e.g., project deadline approaching) can also be set up.
- Human Resources/Admin: Onboarding new employees or contractors can involve repetitive paperwork – automation can send welcome emails, collect digital signatures on forms, and schedule orientation meetings. Scheduling meetings or interviews can be automated with tools that coordinate calendars.
Prioritize the tasks that are high-frequency and rule-based. Those will give you the biggest return on automation. For each potential task, estimate how much time per week is spent on it and how critical it is. This will help you decide what to tackle first in your automation journey. Remember, the goal of identifying opportunities is to find those areas where a small investment in setting up an automation could save a huge amount of time or eliminate a pain point as you grow. By systematically uncovering these areas, you’re laying the groundwork for the step-by-step implementation to follow.
Setting Clear Automation Goals
Once you’ve identified some processes that are ripe for automation, the next step is to set clear goals for what you want to achieve. It’s tempting to dive right in and start automating, but taking a moment to define success criteria will pay off in the long run. Clear goals ensure that your automation efforts actually support your broader scaling objectives and allow you to measure their impact.
Start by asking: What outcome do I expect from automating this process? The answer should be specific and measurable. For example, “Reduce the average customer support email response time from 4 hours to 30 minutes,” or “Handle double the number of leads per week without hiring additional sales reps.” Perhaps the goal is “Eliminate data entry errors in finance reports” or “Save 10 hours per week on manual data updates.” Having these targets helps you choose the right approach and also helps in selecting metrics to track (more on monitoring later).
If your goal is efficiency, quantify it. Is it time saved? Lower error rate? Faster customer issue resolution? If your goal is growth-oriented, maybe you want to increase conversion rates or output. For instance, automating email follow-ups might aim to increase the percentage of leads that schedule a demo. Write these goals down in plain language and ensure they align with your startup’s KPIs (Key Performance Indicators). This step is about linking the micro (a specific automation) to the macro (your business growth targets).
It’s also wise to define the scope of the automation project. Are you aiming to automate an entire end-to-end process, or just a part of it initially? Perhaps Phase 1 is automating the data collection for a report, and Phase 2 might automate the analysis or distribution of that report. Setting phased goals can make large automation projects more manageable and less daunting. Each successful phase will build confidence and momentum for the next.
Another important aspect is setting expectations with your team. If employees are used to the old way of doing things, let them know why you’re implementing an automation and what the goals are. For example, explaining that “the goal of this chatbot is to allow us to answer basic customer questions instantly, so our support team can spend more time solving complex issues” helps everyone understand the purpose. It also frames automation as a positive improvement (removing drudgery) rather than a threat. This clarity goes a long way in getting buy-in from your team, which is crucial for success.
Lastly, consider setting a goal for learning. Especially if this is your first foray into no-code tools or AI, one goal can simply be: “Gain hands-on experience with automation to identify further opportunities.” In other words, an initial pilot automation might be as much about educating yourself and your team as it is about the direct time-saving it brings. With clear goals, you’ll have a beacon to guide your implementation and a benchmark to determine if the automation delivers the value you hoped for. Now, with targets in mind, let’s move into the actual steps of putting no-code AI automation to work in your startup.
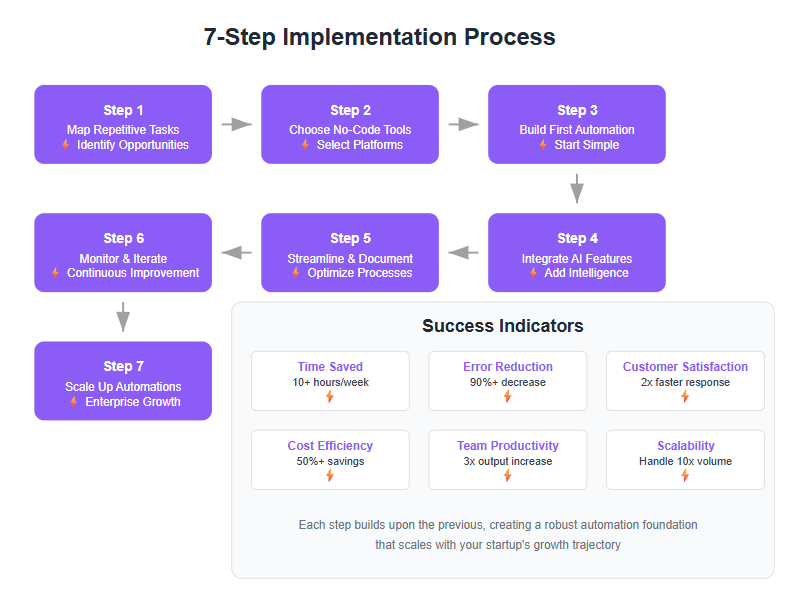
Step 1: Map Out Repetitive Tasks
The first step in our seven-step guide is to map out the repetitive tasks in your startup – essentially creating an automation roadmap. This builds directly on the identification phase. Take the list of candidate tasks you brainstormed and break down each task into a series of steps or a workflow. By mapping it out, you not only get clarity on how the process works, but you also prepare to translate it into an automation.
For each routine task you want to automate, write down the step-by-step procedure as if you were training a new employee to do it. For example, let’s say one task is “Posting our blog updates to all social media accounts.” The manual steps might be: 1) Copy the blog title and link, 2) Open Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, etc., 3) Paste the content with a short message on each, 4) Schedule or post it. Similarly, a task like “Processing incoming orders” might involve: 1) Receive order email, 2) Extract customer info and order details, 3) Enter into our database or Google Sheet, 4) Send confirmation email, 5) Notify fulfillment. Write these down in order.
While mapping, note any decisions or variations. Does the process ever branch? (e.g., “If high-priority customer, do X, otherwise do Y.”) These conditions are important because they will translate into logic for your no-code workflow. Most no-code automation tools allow you to set up conditional rules (if/then branches), so you want to understand the logic of the process. If you find a process has a lot of complex branching, you might choose to simplify it or handle part of it manually initially, depending on tool capabilities. However, many modern no-code platforms are surprisingly adept at handling conditional logic and even utilizing AI for decision steps.
Be thorough in capturing details like: what triggers the process to start, what inputs are needed, what output or result occurs at the end, and who currently performs each step. For instance, “trigger: new support email arrives, input: email content, process: parse email -> determine issue type -> create ticket -> send auto-reply -> assign ticket, output: ticket in system + customer gets response.” By mapping this, you’ve essentially outlined a blueprint that an automation can follow.
This exercise may also reveal inefficiencies or unnecessary steps. Sometimes when you lay out a process, you realize certain steps could be eliminated or simplified even before automating. That’s great – it means you’re not just copying a bad process into an automated form, but actually optimizing it. In fact, experts often say “don’t automate a broken process” – fix the process first, then automate. Mapping helps you do that.
As you map tasks, prioritize them based on the earlier goals. Which mapped process, if automated, would have the biggest positive impact? Perhaps you have 10 processes outlined, but you’ll tackle them one by one. A helpful approach is to start with something relatively simple but impactful. This way, you get a quick win under your belt. For example, a straightforward email alert automation might be simpler to implement than a multi-step customer onboarding flow. The email alert could save a couple hours a week and is easy to set up – a perfect first candidate. Quick wins build confidence and momentum.
By the end of Step 1, you should have a clear map of at least one (if not several) key workflows that you plan to automate, along with details on triggers, steps, and outcomes. Think of this as creating the recipe that your no-code automation “chef” will follow. With this map in hand, we move to selecting the right tools to cook up our automation masterpiece.
Step 2: Choose the Right No-Code Tools
Now that you know what you want to automate, the next step is figuring out how to do it – which means choosing the right no-code tools for the job. The good news is there’s an entire ecosystem of no-code platforms and AI services available in 2025, each with different strengths. The key is to match the tool to your specific task and your team’s comfort level.
First, consider workflow automation platforms. These are like the glue that connects different apps and handles step-by-step processes. Zapier is one of the most popular ones, allowing you to integrate over 5,000 apps and set up “if this, then that” workflows (called Zaps) easily. For example, you can create a Zap that says: “If a new row is added in our Google Sheets (maybe via a form submission), then send an email to our team and also add the data to MailChimp.” Zapier’s strength is its vast integrations and ease of use – great for many business processes. Alternatives include Make(formerly Integromat), which offers more advanced multi-step flows and branching, and IFTTT (If This Then That) for simpler one-to-one automations. These tools are ideal for tasks like moving data between systems, sending notifications, scheduling tasks, and so on. They require no coding – you simply connect accounts and fill in fields through a guided interface. Each platform's environment allows you to design, customize, or even clone workflows, making it easy to tailor the platform's features to your specific automation needs.
Next, look at no-code app builders if your scaling needs involve creating internal tools or customer-facing applications. Platforms like Bubble, Adalo, or Glidelet you build full-fledged web or mobile applications with drag-and-drop elements and logic. For instance, if you need a custom CRM or a client portal and don’t want to code it from scratch, a no-code app builder can be a lifesaver. Bubble, in particular, is known for its flexibility; non-technical founders have built SaaS products entirely on Bubble. These platforms often include workflow automation within them – for example, in Bubble you can design workflows triggered by user actions in your app (like sending a welcome email when someone signs up). No-code solutions help startups bring products to market faster, with development being up to 10 times faster than traditional approaches. If scaling your startup means providing a new digital service or tool, a no-code platform might allow you to launch it without hiring a dev team.
Another category is AI-specific no-code tools. These have exploded recently. They include things like no-code chatbot builders (e.g., ManyChat for integrating AI chatbots on your website or Facebook page), AI analytics platforms (like Akkio or MonkeyLearn that let you feed in data and get predictions or text analysis via an interface), and tools integrated with GPT (like OpenAI’s ChatGPT plugins accessible through Zapier or other no-code frontends). For example, Akkio offers AI-powered data analytics with an easy setup: you connect your dataset and choose what you want to predict, and it handles the machine learning behind the scenes. If one of your identified tasks was, say, analyzing customer feedback to tag sentiment, a tool like MonkeyLearn can use AI to classify text without you writing code. For customer service, there are no-code platforms like Intercom or Zendesk that have AI add-ons to automate responses and routing. Some workflow tools (as mentioned, Zapier now has built-in AI features and can connect to OpenAI) allow you to include an AI step – for instance, “take this customer message and run it through OpenAI to summarize it, then proceed.”
When choosing tools, also consider integration with what you already use. If your startup runs on Google Workspace, many no-code automations can be done with Google’s Apps Script (low-code) or using tools that specialize in Google integration. If you’re on Microsoft 365, their Power Automate platform is an option (though more low-code). There are even specialized no-code tools for specific domains: e.g., Zapier for Startups programs or ones tailored to e-commerce like Shopify Flow (for Shopify stores to automate tasks). Evaluate whether the tool can connect to your existing software stack easily.
Ease of use and community support matter too. As a startup founder or team, you want a tool that you can pick up quickly. Zapier, for example, has an extensive library of templates (pre-made automation recipes) and a large community sharing ideas, which can flatten the learning curve. Bubble has many tutorials and a passionate user base. Check out documentation and maybe a demo or tutorial for a few tools to gauge which one “clicks” for you. Many have free trials or free tiers – take advantage of that to do a test run.
Security and reliability should factor into your choice as well, especially if dealing with sensitive data. Established no-code platforms will have information on data handling and compliance. Ensure that any AI service you use for sensitive tasks has proper data privacy measures (for instance, if using an AI to process customer data, verify it doesn’t store or misuse that data).
To sum it up, match the tool to the task. Use workflow automation platforms for connecting apps and simple processes, no-code app builders if you need to build custom solutions or interfaces, and specialized no-code AI tools for tasks involving data analysis, predictions, or natural language processing. Often, you might use a combination. For example, you might use a Bubble app as a front-end, Zapier to integrate Bubble with your email marketing software, and an AI service integrated via Zapier to analyze some text in the workflow. This may sound complex, but each piece is handled with no-code configuration, and you as the “conductor” just ensure they play in harmony. Once you’ve picked the tools that suit your needs, it’s time to actually create your first automation.
Step 3: Build Your First Automation
With your workflow mapped and tools in hand, it’s time for the exciting part: building your first automation. Start with a single, well-defined process – preferably the one you identified as high-impact and relatively straightforward. The goal here is to get a working automation up and running, even if it’s small, to prove the concept and gain confidence.
Let’s walk through an example to illustrate the process. Suppose you decided the first thing to automate is lead handling – specifically, when someone fills out a form on your website, you want to: (a) receive an immediate notification in Slack or email, (b) add the lead’s details to your CRM or Google Sheet, and (c) send a quick personalized thank-you email to the prospect. Doing all that manually for each lead is tedious; automating it will save time and ensure no lead falls through the cracks.
Using a tool like Zapier, you would create a new workflow (in Zapier terms, a “Zap”). The trigger would be “New form submission received” (for instance, if you use Google Forms or Typeform or your website form sends an email – Zapier can trigger off many sources). You’d connect Zapier to that form app. Next, you add actions: The first action could be “Send channel message in Slack” – you choose your Slack workspace and channel, then craft a message template like “New lead from {{Name}} ({{Email}}) came in!”. The placeholders get filled with data from the form automatically. The second action might be “Create spreadsheet row” or “Create contact in CRM” – you map the form fields to columns in your Google Sheet or fields in your CRM (again, all done via dropdowns and field mapping in the interface, no code). The third action: “Send email” via Gmail or another email service. Here you could drop in the person’s name in a pre-written thank you message. Once these steps are configured, you turn on the Zap. Now test it out: submit a dummy form entry and watch as – voila! – within seconds Slack pings you, the spreadsheet updates, and an email is sent to the test address. You’ve built your first no-code automation!
During the building process, take advantage of templates or pre-built integrations the platform offers. Zapier and others often have templates for common scenarios (e.g., “Add new Typeform responses to MailChimp as subscribers”). You can use these as a starting point and modify as needed, which accelerates setup. Also, do use the testing features. Most platforms allow you to test each step with sample data to ensure it’s working as expected. It’s easier to catch and fix any misconfigured field in testing than after it’s running live.
Don’t be discouraged if you hit a snag. Perhaps the data isn’t in the format you need, or you realize you need an extra step (like formatting a date or splitting a full name into first and last). Many no-code tools have built-in utilities for these transformations. For instance, they might have a “Formatter” action to tweak text, dates, or numbers. If something seems not possible at first, a quick search in the tool’s help center or forums might reveal a clever solution or workaround discovered by other users. The no-code community is usually very supportive.
When building, keep the KISS principle in mind – “Keep It Simple, Startup!” (a friendly adaptation of the classic saying). You don’t want to over-engineer your first automation. Stick to the core steps needed to meet your goal. If the initial success of this workflow inspires more ideas (e.g., “Oh, I could also automatically schedule a calendar event for a follow-up call!”), jot those ideas down for later. It’s better to get one solid automation working reliably before adding bells and whistles or moving to the next project.
After you’ve built and tested your first automation, celebrate it! It may seem small, but this is a significant milestone. You’ve effectively hired a tireless assistant (for a lot cheaper) that will work 24/7 without complaining. Even a basic automation can save countless hours over a year. Plus, you’ve proven to yourself and perhaps your team that no-code AI automation is not some distant dream – it’s here and it works for your startup. This victory will make it easier to undertake more complex automations, like the ones involving AI which we’ll tackle next.
Step 4: Integrate AI for Advanced Tasks
Once you have some fundamental automation running, it’s time to level up by integrating AI for more advanced tasks. This is where your startup can start reaping the benefits of artificial intelligence – think of it as moving from basic “if-this-then-that” automation to intelligent automation. AI can handle tasks that involve understanding content, making predictions, or personalizing decisions in a way standard rules-based automation cannot.
Identify areas from your earlier mapping where a decision or analysis is usually done by a person because it requires interpretation. Common examples include: categorizing a customer support query by its sentiment or topic, prioritizing leads based on likelihood to convert, personalizing a marketing message based on user behavior, or analyzing large data sets for patterns. These are perfect candidates for AI.
To integrate AI, you don’t need to build an AI model from scratch (thankfully, since that would require coding and data science). Instead, leverage pre-built AI services accessible via no-code tools. For instance, if you want to implement a customer support chatbot on your website, platforms like Landbot, Tars, or even your existing customer service software (many have AI chatbot add-ons) allow you to design conversational flows visually and then plug in an AI like GPT-4 to handle understanding and responding to user questions. You’ll configure the bot with a no-code interface: adding common questions, desired responses, and connecting it to your knowledge base. The underlying AI ensures that even if a customer’s query isn’t a word-for-word match to a preset question, the bot can still figure out the intent and respond appropriately.
Another scenario – let’s say you have an influx of user feedback or survey responses and you normally read through them to gauge satisfaction. This is time-consuming as volume grows. Here you can use a no-code AI text analysis tool. For example, MonkeyLearn or Google Cloud’s AutoML (with a no-code front-end) can take a bunch of text entries and automatically tag them as Positive/Neutral/Negative sentiment, or categorize them by topic. Via a platform like Zapier, you could set up a flow: whenever a new feedback comes in (trigger), an action sends the text to an AI sentiment analysis API (these integrations exist with no-code steps), then based on the result (e.g., negative sentiment), you could trigger another action like alerting a manager for follow-up. The AI here provides the “brain” to understand the content without a human reading it.
AI can also help in decision-making processes. For example, integrating a tool like OpenAI’s GPT via no-code can enable you to do things like generate a draft response to an email inquiry. Suppose part of your workflow is responding to common customer questions. You can have a step that sends the question to GPT through a no-code connector, and it returns a draft answer which your automation can email out or maybe send to a human for quick review then send. This drastically speeds up response times. Startups have begun using GPT-like services to generate content (marketing copy, code snippets, reports) by giving it prompts filled with the latest data, all automated behind the scenes.
One real example: a business operations team integrated ChatGPT via Zapier to generate a personalized follow-up email after a sales call is logged. The automation pulls key details (like the product of interest, company name, etc.) and asks GPT to draft a friendly follow-up email. The sales rep just reviews it and hits send. It saved the team dozens of hours and ensured quality, consistent messaging. That kind of AI assist is invaluable when scaling, because it means you maintain a personal touch (through AI’s capability to vary and contextualize language) without needing an army of content writers or support agents.
While integrating AI, a few tips: start simple and monitor outputs. AI is powerful but not perfect. For instance, an AI might occasionally misclassify something or give an odd answer. Initially, keep a human in the loop if the task is high-stakes. Maybe you have the AI make a recommendation or draft, and a person approves it. As confidence in the AI’s performance grows, you can automate the approval too. Many no-code AI platforms provide accuracy metrics or allow you to review a percentage of outputs. Testing AI applications can involve unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. These steps ensure that the AI performs as expected and integrates seamlessly into your workflows.
Also, ensure you feed the AI quality data. If you’re using an AI model for predictions (like which leads are most likely to convert), you’ll either use a pre-trained model or train one by uploading historical data via a no-code interface. Make sure that data is clean and representative. The phrase “garbage in, garbage out” applies to AI as much as anything. The better the input and training, the better the AI’s output.
Finally, always align AI usage with your business goals and ethics. For instance, using AI to personalize user experiences (like recommended products or tailored emails) can significantly boost engagement, but be mindful of privacy and not overstepping in a way that feels invasive to users. Used thoughtfully, AI will be like a supercharged extension of your team – handling complex or large-scale cognitive tasks so your startup can serve more people, more efficiently, without losing the personal touch that early customers love.
Step 5: Streamline and Document Processes
By this stage, you’ve likely implemented one or several automations and perhaps added some AI magic to them. Now it’s crucial to streamline and document these new processes. As your startup scales, well-documented and optimized processes ensure that growth doesn’t devolve into chaos. This step is about integrating automation into your operations smoothly and setting up your team for long-term success.
First, streamline: Review the automations you’ve built and see if they are running as efficiently as possible. Are there any redundant steps that could be removed now that the process is automated? For example, maybe you were keeping a manual log of support tickets, but your new system automatically logs and tracks them, so you can stop the old logging practice. Simplify the workflow wherever possible. Often, automating reveals opportunities to standardize inputs or remove unnecessary approvals or checkpoints. If the AI chatbot is reliably answering basic questions, perhaps you no longer need a support agent to pre-screen those tickets at all – they can focus only on complex cases. Thus, you might combine or eliminate roles or steps, effectively streamlining the whole operation.
Ensure that the automations are properly integrated with each other and with any remaining manual steps. If one automation feeds data into another system where a person then picks it up, double-check that the handoff is smooth. Sometimes small adjustments (like tweaking the format of data, or adding a notification for the person) can make a big difference in usability. The goal is to create a seamless hybrid of automated and human workflows, where each does what it’s best at. For instance, your process might now be: AI categorizes incoming tasks, automation assigns or resolves them, and humans address only the ones flagged as complex – this synergy can dramatically increase throughput.
Next, document everything. It might be tempting to skip documentation (“it’s automated, it just works!”), but resist that temptation. Write clear documentation on how each automated process works, including: what triggers it, what steps it performs, which tools are involved, and what to do if something goes wrong. Remember, as you scale your startup, new team members will come on board, and existing ones might change roles. Having a reference guide for your automations ensures continuity. For example, if an alert stops coming or data isn’t syncing, someone should know where to check – is it the Zapier workflow? the API key? – without having to reverse-engineer everything.
Documenting also includes maintaining an updated list of all the no-code tools and services you’re using, along with their access credentials (securely stored, of course) and any subscription info. This is important for budgeting and for tech management – you don’t want an automation to fail just because a trial ended or a token expired and no one realized it.
Involve your team in the documentation process. Encourage those who work with the automation to contribute their perspective. For example, the support team can note how the automated chatbot escalates issues to them, and perhaps suggest improvements. Documentation can be a living thing – a Google Doc or Notion page that everyone can comment on and update when something changes. Keep it simple and to-the-point, though. A concise process doc or flowchart is more likely to be used than a 50-page manual. Screenshots of your no-code workflow configurations or a diagram can be very helpful in the docs.
As part of streamlining and documenting, it’s also a good time to establish an “automation owner” or a point person. This is someone (maybe you, or someone on your team) responsible for periodically checking that automations are running well, updating them if processes change, and being the go-to for any issues. This doesn’t mean a heavy workload – often automations run in the background without intervention – but having clear ownership prevents automations from being forgotten and ensures they continue to align with your evolving business processes.
By the end of Step 5, your automated workflows should be well-oiled and well-documented parts of your operations. You’ve essentially created a playbook for how your startup uses no-code AI automation in day-to-day work. This not only helps current operations but also serves as a training and onboarding tool as your team grows. Streamlined processes with proper documentation act like a sturdy backbone for your scaling efforts, keeping everything aligned and efficient.
Step 6: Monitor, Measure, and Iterate
Automation isn’t a “set it and forget it” deal, especially in a dynamic startup environment. Step 6 is all about monitoring the performance of your automations, measuring their impact, and iterating on them for continuous improvement. This is where we circle back to the goals we set earlier and see if we’re hitting them, and how we can refine our approach.
Start by establishing some key metrics for each automated process. These could include quantitative metrics like time saved, reduction in errors, increased throughput (e.g., number of support tickets handled per day), conversion rate changes, or cost savings. Qualitative feedback can be a metric too, such as team satisfaction (are people less stressed now?) or customer satisfaction (are customers happier with faster responses?). For example, if you automated lead follow-ups, track metrics like: How many leads are we able to manage per week now vs. before? Has the lead-to-customer conversion rate improved because follow-ups are prompt and consistent? If you rolled out an AI chatbot, measure things like: Ticket volume handled by bot vs. human, average response time, and maybe a customer survey question like “Was your issue resolved effectively?”.
Many no-code tools and platforms have monitoring and logging features built-in. Zapier, for instance, will show you task history – you can see every time your Zap ran and if it succeeded. AI platforms might have dashboards showing how many predictions or API calls were made, and sometimes the confidence levels of predictions. Keep an eye on these. It’s wise to set up alerts for failures: if an automation fails or an error occurs, ensure you or someone is notified. You might even automate the monitoring – e.g., if a Zap fails, Zapier can alert you via email or Slack. That way, you can respond quickly if something breaks.
Regularly review the data. Perhaps set a calendar reminder monthly or quarterly to assess: Are the automations still delivering the expected value? Did we meet our goal of, say, cutting response time by 75%? If not, why? Maybe the bot is fine, but we discovered another bottleneck. Or perhaps we overshot – we cut time by 90%, which is great! Maybe the goal can be more ambitious or we can redirect saved time to other initiatives. In essence, treat your automation implementations like any other product – they have KPIs and you should evaluate their ROI (return on investment).
Armed with this information, iterate. This could mean fine-tuning an existing automation. For instance, if the AI classification of customer inquiries is only 85% accurate and causing a few hiccups, you might retrain it with more data or adjust the categories. Or if you notice your social media posts (automated) are going out at odd times, you might adjust the schedule logic. Iteration might also mean expanding the automation’s scope. Perhaps your initial workflow handled domestic orders, and now you can tweak it to handle international orders too. Or if one step is still manual, consider automating that now.
Iteration can also involve upgrading tools as your needs grow. Maybe you started on a free tier of a platform and hit some limits (like number of tasks per month). That’s a good problem – it means you’re actively using it. Consider whether upgrading or even switching to a more robust tool is warranted as you scale. Luckily, no-code platforms are generally quite scalable themselves – they are built to handle big volumes (Zapier and others serve enterprises too). But always evaluate if the platform you chose is still the best fit; new tools come out often, and features improve rapidly in this space.
It’s also beneficial to gather feedback from your team during this monitoring phase. Are they happy with the automations? Maybe the sales team says, “The automated lead assignment is great, but could we also get it to pull some LinkedIn data on the lead to prioritize better?” That might lead you to incorporate another tool or step (some no-code data enrichment service, for example). Or perhaps the team noticed that at a certain time of day something glitches due to how data is synced – that’s actionable feedback to refine the process.
This step is an ongoing loop of measure -> learn -> improve. Each iteration not only makes the current automation better but also teaches you more about what works best for your startup’s workflows. In a sense, your organization is learning how to work alongside automation. Companies that scale successfully often establish a culture of continuous improvement with automation: it’s not a one-time project, but a capability they constantly leverage and enhance. By staying vigilant and proactive through monitoring and iteration, you ensure that your no-code AI automations continue to deliver maximum value as your startup grows and evolves.
Step 7: Scale Up Your Automations
With multiple efficient automations in place and a process for continuous improvement, the final step is to scale up your automations themselves, in tandem with your business growth. This means both expanding automation to new areas of your startup and ensuring your automation infrastructure can handle increasing load.
Start by reflecting on your success so far: which areas of the business have benefitted most from automation? Perhaps your customer support is now largely automated and running smoothly. Meanwhile, maybe your marketing team is doing a lot of things manually still, or your data analysis is still manual. Identify the next set of processes or departments that would gain from automation. This could be revisiting the list of opportunities you made earlier and picking up those that were lower priority. Or it could be new processes that emerged as your startup introduced new features or services.
As you scale, think cross-functionally. Often the biggest wins in automation come from linking different parts of the business. For example, when a sales deal is closed, that information could automatically flow to finance (for invoicing), to customer success (for onboarding), and to analytics (for revenue tracking). Initially you might have automated within silos (just sales tasks, just support tasks), but scaling might involve connecting these silos. No-code tools often excel at this integration – acting as a bridge between teams. By automating hand-offs between departments, you reduce delays and miscommunications, which is vital as more people get involved in processes during growth.
Also consider scaling the complexity of what you automate. Early on, you might have shied away from automating very complex or critical processes. But now that your team is comfortable and you have some automation champions, you can tackle more sophisticated workflows. For instance, you might build a fully automated onboarding sequence for new customers that involves multiple touches over time (emails, tutorials, check-in messages) tailored by AI based on user behavior. Or you might implement an AI-driven recommendation engine on your product to upsell or cross-sell features – using no-code integration to plug a service into your app or website. These advanced automations can drive exponential growth or efficiency gains, but they might require careful design. Thankfully, with the experience you’ve built, you’re much better positioned to create and manage them.
Ensuring the infrastructure scales is another aspect. As your user base and data volume grow, make sure your no-code tools are keeping up. Most reputable no-code platforms can handle substantial scale (many have enterprise clients), but you may need to adjust your plan (as mentioned, moving from a free or basic plan to a professional one with higher limits). Monitor if any automations are nearing usage limits or if tasks are queueing up. For instance, if you suddenly get 10x the number of form submissions, Zapier might queue tasks if you’re on a lower plan, causing delays. Upgrading will allow concurrency or higher throughput. Budget for these increases – it’s usually still far cheaper than hiring equivalent manpower. It’s a good sign: if you’re paying a bit more for automation tools, it likely means your business is scaling!
At this stage, you might also explore additional tools or custom solutions if needed. Occasionally, as companies scale, they find some no-code solutions might hit a wall for very specific needs, and that’s when a bit of low-code or custom code might come in. For example, you might integrate a custom script or a specialized service via APIs for a niche task. But the beauty is you can often still connect those via your no-code platform (Zapier’s “Webhook” feature, for instance, can interface with custom endpoints). In essence, no-code and code can coexist – no-code doing 90% of the heavy lifting, and a snippet of code for the 10% unique to your business. That’s far more efficient than coding everything from scratch.
A crucial part of scaling up is also scaling the team’s mindset and skills. By now, hopefully your team sees automation as a friendly colleague, not a threat. Continue to train and encourage team members to propose automation ideas. You might even run a workshop or hackathon where each team member automates one tiny thing they hate doing – it could be fun and empowering. The more people in your startup who are automation-savvy, the more scaling will be part of your culture. When everyone has the mentality of “How can we automate this to handle 10x more?”, your startup is truly poised for hypergrowth.
In conclusion of this step, scaling up your automations means making automation an integral, ever-expanding part of your business strategy. It’s about breadth (more processes) and depth (more complex tasks) of automation, ensuring your startup can handle growth in stride. By this point, you should be seeing that tasks which would have required whole new teams are being managed by your no-code AI arsenal, and your human team is operating at a higher level, driving innovation and serving customers with a personal touch where it matters most. You’ve built a scalable foundation – now it’s about extending it everywhere it can add value.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
Embracing no-code AI automation is transformative, but it doesn’t mean there won’t be bumps along the road. As you implement the steps above, it’s important to be aware of common challenges and misunderstandings, and know how to address them to ensure long-term success.
One challenge is misalignment or misuse of tools. With so many tools out there, it’s possible to pick one that isn’t the perfect fit or to over-automate something in a way that creates confusion. For instance, automating a process that wasn’t well understood to begin with can lead to mistakes happening faster! To avoid this, always double-check that a process is clearly defined and stable before automating (remember the mapping in Step 1). If issues arise, don’t be afraid to pause an automation, fix the process or rules, and then resume. It’s better to get it right than to let a faulty automation run wild.
Another concern teams often have is fear of automation replacing jobs or reducing the human element. It’s crucial to frame automation as a means to amplify human work, not replace it. As noted in a Harvard Business Review piece, while the purpose of automation is efficiency, humans remain essential for strategic and creative tasks; automation protects businesses from inefficiency but doesn’t eliminate the need for human insight. Communicate with your team that the goal is to remove drudgery, not their jobs. In fact, by automating, the company can grow faster, potentially creating more interesting roles and opportunities. Encourage employees to see automation as a collaboration: the robot does the boring part, you do the engaging part. Over time, as they feel the relief of tedious tasks lifted off their shoulders, this fear usually subsides into enthusiasm.
There’s also the challenge of keeping automations updated as things change. Startups pivot and processes evolve. An automation set up today might need tweaking a few months down the line if you change a tool (say you move from one CRM to another) or alter a workflow. This is where having that documentation and ownership helps. Periodically review automations to see if they still align with current processes. Make it a habit that whenever a team changes a process, they also consider, “does our automation need to change too?” Keeping the human and automated parts in sync ensures you don’t end up with legacy rules running on autopilot that no longer apply.
Security and data privacy is another area to keep an eye on. When using multiple tools and automating data flow between them, be mindful of what data is going where. Use the built-in security features of platforms (like encryption, access controls) and avoid exposing sensitive information unnecessarily. For example, if you’re automating something with personal customer data, ensure the services you use are reputable and compliant with regulations like GDPR if applicable. Most major no-code platforms offer compliance info; reviewing that can build trust in using them. It’s also wise to limit access: not every team member needs to access every automation tool or data set. Use roles and permissions to control who can tweak workflows or see certain data.
One practical challenge might be hitting limits or encountering a scenario where no-code tools seem not to handle something. Before assuming “we can’t automate this,” reach out to the community or support forums. Often, someone has found a clever solution or a workaround. The pace of improvement in no-code tools is rapid – new features roll out frequently, especially with the demand rising. That said, sometimes you might conclude that a particular complex process might remain partially manual for now. That’s okay. Focus on what yields the most benefit. Even partial automation can be a huge win.
Finally, ensure you have fallback plans. If an automation fails, is there an alert and a plan for handling things manually until it’s fixed? For critical customer-facing processes, design with fail-safes. For example, if your automated system for customer support goes down, have instructions for support staff to step in or have a simplified backup process (maybe an email inbox they can monitor in the interim). These contingencies mean a glitch won’t hurt your business reputation.
By being proactive about these challenges – aligning tools, addressing team concerns, updating processes, keeping an eye on security, and planning for contingencies – you build trustworthiness around your automation strategy. Your team and customers will trust that while you’re embracing cutting-edge no-code AI solutions, you’re doing so responsibly and intelligently. Overcoming these hurdles ensures that automation continues to be a boon to your startup and not a source of new problems. In fact, handling them well is part of the Experience and Authority you develop in using these technologies; it’s how you become an organization where automation is in the DNA, fueling growth reliably and sustainably.
Popular No-Code AI Tools for Startups
Throughout this guide, we’ve mentioned various tools and platforms. Here we’ll summarize some of the popular no-code AI and automation tools that startups are leveraging to scale, along with what they’re commonly used for.
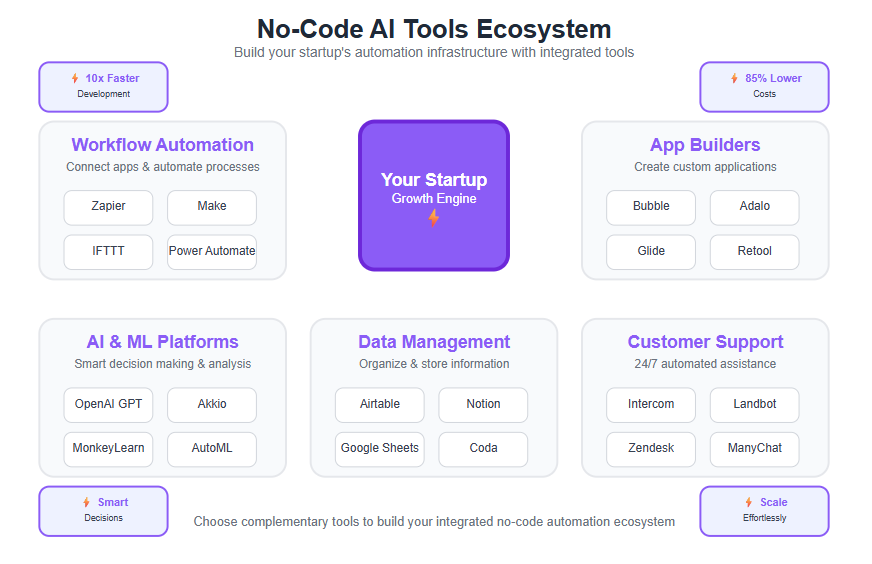
This can serve as a mini-toolkit reference as you plan your automation strategy:
- Zapier: A powerhouse for connecting different apps and automating workflows. It supports thousands of apps (from Gmail to Slack to Salesforce) and is often the first choice for easy “if this, then that” automations. Great for things like moving data between systems, sending automated notifications, and simple bot tasks. Zapier has also introduced Zapier Interfaces and AI integrations, making it easier to include AI like ChatGPT in your Zaps. A competitor worth noting is Make (Integromat), which offers more visual flow building and can be more flexible for complex scenarios.
- Bubble: A no-code platform for building web applications. If you need to create a custom tool (like a web app, customer portal, or even a small SaaS product), Bubble provides a canvas to design the interface and the logic behind it. Non-technical founders have built fully scalable startups on Bubble. It also has workflow automation within it, and you can connect it to any number of APIs or plugins (including AI services) to extend its power. Other similar app builders include Adalo (more for mobile apps) and Retoolor Airplane.dev for internal tools.
- Airtable: Part spreadsheet, part database, Airtable is a favorite for organizing data in startups. It’s no-code in that you can build relational databases with a spreadsheet-like interface. What makes Airtable powerful for automation is its ability to integrate with Zapier/Make or use Airtable Automations (built-in feature) to trigger actions when data changes. Many startups use Airtable as a lightweight CRM, content calendar, or project tracker and automate interactions like sending emails when a status changes, etc. Similarly, Notionnow has an API and some automation capabilities, and Codais another doc/spreadsheet platform with automation features.
- Chatbot Builders (Landbot, Intercom, etc.): For customer-facing automation, tools like Landbot allow you to create conversational chatbots visually. Intercom (a customer messaging platform) offers Resolution Bot for automated answers. These often have AI under the hood to understand variations of questions. Drift and Tars are others that focus on marketing/sales chatbots. They often integrate with your site by just embedding a snippet of code, and you design the conversation flow in a no-code editor.
- AI Content and Image Generation Tools: If part of scaling involves producing more content (blogs, social media, marketing materials), AI writing assistants like Copy.ai, Jasper, or OpenAI’s GPT-4 via a simple no-code front-end can help generate drafts of marketing copy, product descriptions, etc. There are also AI image generation tools (like DALL-E, Midjourney through no-code interfaces) to create graphics or design ideas. These can be semi-automated; for example, some startups connect their CMS to GPT so that a first draft of a blog on a trending topic is generated automatically for the content team to refine.
- Analytics and Machine Learning Platforms: For data-heavy tasks, platforms like Akkio (mentioned earlier) let you do things like upload sales data and create a prediction model, all via no-code steps. Google’s AutoML and Microsoft’s AI Builder (in Power Platform) are also aimed at no-code creation of ML models (though some UI familiarity is needed). These are useful for things like churn prediction, LTV (lifetime value) prediction, or any custom model where you have data but no data science team. Once a model is made, you integrate it in your processes (for instance, via an API call in Zapier or a direct integration if they offer one).
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation) Tools: RPA tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or newer no-code ones like Electronique focus on automating tasks that involve user interfaces – for example, clicking buttons and copying info between legacy systems. They are a bit more heavy-duty and often used in enterprise, but if your startup finds itself doing a lot of manual work on desktop apps or websites without APIs, an RPA bot can mimic those actions. Some RPA platforms are making efforts to be more no-code friendly, though they may require some training to use effectively.
- Workflow and Project Automation: For internal team workflows, products like Trello, Asana, Monday.com have automation features (e.g., move a card and it pings someone or updates a field). If your team already lives in one of these tools, using their built-in automation or bots can be a quick win. Similarly, Slack has Workflow Builder for simple automations (like a button that collects info and posts somewhere) – no-code and good for internal QOL (quality of life) improvements.
Each of these tools addresses different needs: integration, app building, AI content, data analysis, UI automation, and so on. The best part is many of them can work together. For instance, you might use Airtable to log data, Zapier to react to new entries and invoke an AI on Akkio, then post results to Slack – a chain of no-code tools, each doing what it’s best at.
When choosing from this smorgasbord, always align with the problem you’re trying to solve. It’s easy to get shiny object syndrome with tools, but the most successful startups pick a few core ones that fit their workflows and become adept at those. The tools listed above are popular for a reason – they’ve proven themselves in many scenarios and have strong communities. Leveraging them can give your startup a quick boost on the automation journey. The combination of these tools, applied thoughtfully, essentially gives you superpowers to scale faster and smarter than would have been possible even a few years ago.
FAQs
Q1: What is no-code AI automation in simple terms?
A1: No-code AI automation means using tools that let you create automated processes and leverage artificial intelligence without writing any code. “No-code” platforms provide visual interfaces (like drag-and-drop editors or form-based settings) so you can build apps or workflows. When we add “AI automation”, it implies these processes can include AI capabilities – for example, understanding language or making predictions. In simple terms, it’s like telling a computer what to do in plain English or via diagrams, and having it handle tasks for you automatically. This allows people who aren’t programmers to automate parts of their business and use AI features through user-friendly tools. It’s the equivalent of giving instructions to a very smart assistant: you set up the instructions once, and then the assistant (the no-code tool + AI) carries them out whenever needed.
Q2: How can no-code automation help my startup scale effectively?
A2: No-code automation helps your startup scale by enabling you to do more with less. It takes over repetitive, time-consuming tasks, which means your team can handle a larger workload without burning out or making mistakes due to fatigue. For instance, if your customer base doubles, an automated customer onboarding sequence ensures each new customer still gets timely emails and support resources without you hiring extra staff. It ensures consistency and reliability – processes run the same optimal way every time, even as volume increases. Furthermore, automation can improve your response times (e.g., leads get followed up within minutes, support queries answered instantly by bots), which boosts customer satisfaction and conversion rates. All these factors allow growth (more users, more revenue) without a corresponding linear growth in costs or manpower. In fact, companies now consider automation a must-have for efficient growth because it improves both business performance and the employee experience. In short, automation lays the groundwork so your operations can expand smoothly and quickly.
Q3: Do I need any technical skills to implement no-code AI automations?
A3: Not in the traditional sense of programming, no. The whole idea of no-code tools is that they are accessible to non-technical people. If you can use common software like spreadsheets or presentation apps, you can likely figure out no-code platforms with a bit of learning. They use visual editors, toggles, and simple logic (like filling out “when X happens, do Y” rules). That said, a bit of tech-savviness or willingness to learn will go a long way. You might need to familiarize yourself with concepts like APIs (in very user-friendly terms) or how data flows between apps. Most platforms have great tutorials and templates. For the AI part, you also don’t need to know the ins and outs of machine learning – the tools abstract that complexity. You might choose a model or toggle an AI feature on, but you won’t be writing algorithms. It’s similar to how you don’t need to know how an engine works to drive a car – but you do learn the steering, pedals, and rules of the road. In summary: no coding required, but be ready to think logically and learn the platform’s interface. Many non-engineers (marketing folks, ops managers, etc.) successfully build extensive automations after just a few days or weeks of exploration.
Q4: What are some examples of tasks a startup should automate first?
A4: Great candidates for first automations are tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and frequent. Some examples include:
- Lead management: Automatically adding new leads (from your website or ads) to a CRM or spreadsheet, and sending them an intro email or notifying a salesperson. This ensures no lead is missed and they get a quick response.
- Email follow-ups: If you find yourself or your team sending the same type of emails over and over (like FAQs to new users, payment reminders, thank you notes), that can be templated and automated with personalization fields.
- Data entry and reporting: For instance, copying data from one system to another – say, compiling weekly metrics from various sources into a report. This is tedious and error-prone for a human, but easy for an automation to do at a scheduled time.
- Social media and content scheduling: Use automation to publish posts across platforms when you release a new blog or update, rather than doing each manually.
- Customer support FAQs: Set up a chatbot or even an automated email responder that addresses common questions (e.g., “How do I reset my password?”) with links to your help docs. This can deflect a significant chunk of repetitive support tickets.
Basically, look at where your team spends a lot of time on low-value tasks – those are your low-hanging fruits for automation. By tackling these first, you free up time and see immediate benefits, which can then fund and motivate more complex automations.
Q5: Can no-code automations really handle core business processes reliably?
A5: Yes, no-code automations have matured to the point where they are used for many core processes in businesses around the world – but with some caveats and good practices. Reliability often comes down to how well you design and monitor the automation. No-code tools themselves (like Zapier, Bubble, etc.) are robust platforms with uptime typically above 99%. They handle millions of transactions for users daily. For example, companies use Zapier to process e-commerce orders and Bubble to run entire online services. If set up correctly, an automated process can actually be more reliable than a manual one, since it won’t forget steps or get tired. However, you need to ensure things like error handling are in place. For instance, if an email fails to send, does the system retry or alert someone? During initial setup, test thoroughly with sample data. Once live, keep an eye (especially early on) to catch any unexpected behavior. Over time, you’ll trust it more as it proves itself. Many startups reach a point where automation is the backbone of their operations, and they only intervene when edge cases or exceptions occur. So in short: yes, they can be very reliable for core processes, as long as they’re well-planned and you maintain some oversight (at least initially). It’s also wise to have backups or manual fallback steps for critical operations (like a manual override) just in case, which is a standard best practice even for coded systems.
Q6: Is no-code AI automation secure for my business data?
A6: Security is a valid concern whenever you’re dealing with business or customer data. Reputable no-code platforms invest heavily in security measures – after all, their reputation depends on it. For example, most use encryption for data in transit and at rest, undergo security audits, and comply with regulations (like GDPR, SOC 2, etc.). When you connect apps through a platform like Zapier, the credentials are usually stored encrypted, and the platform doesn’t alter your data beyond routing it as instructed. That said, you should:
- Choose well-known, trusted platforms that have clear security and privacy policies.
- Use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication for all these services to protect your access.
- Limit who on your team has access to create or edit automations, especially those touching sensitive data.
- Avoid sending extremely sensitive data through too many third parties if possible. For instance, you might not want an automation to handle raw credit card numbers or personal health info unless the tools are certified for that.
Also, consider where the AI comes into play. If you’re using an AI service to analyze data, check their data usage policy – some AI APIs might log or use your data to improve their models (OpenAI has options to opt-out of data retention for example). Make sure that aligns with your privacy needs. In summary, no-code tools can be used securely, but it’s important to implement them with the same caution you would any IT solution: follow best practices and stay informed about the tools’ security features. Many startups successfully handle sensitive operations with no-code workflows by doing just that.
Q7: Will no-code automation eliminate the need for developers in my startup?
A7: No-code automation will reduce the dependency on developers for many tasks, but it doesn’t entirely eliminate the need for technical expertise in the long run – especially as your startup scales and your products themselves might require custom development. What it does is empower non-developers to execute ideas and run operations without always waiting for engineering bandwidth. In the early stages, this can significantly accelerate progress and allow your dev team (if you have one) to focus on the truly unique parts of your product. As you grow, you might still need developers to build your core product or to extend no-code tools in ways that are specific to your business. However, even those developers will thank you for automating the tedious parts of integration and admin work! Essentially, no-code and developers complement each other: no-code covers the common groundwork and internal tooling quickly, while developers tackle the differentiated, complex stuff that gives your startup its competitive edge. In some cases, you might hire a developer to maintain the automation systems or build custom integrations as you scale. So think of no-code as a force multiplier – it lifts a lot of weight off your engineering needs, but doesn’t entirely replace the value of having technical talent for strategy and product development. It does mean that you might hire fewer developers than otherwise and can postpone that hiring until you truly need it. Many startups have reached significant revenue milestones with a team of “business” folks leveraging no-code, before ever bringing in full-time engineers, which shows how far you can get.
Conclusion
Scaling your startup with no-code AI automations is like turbocharging your business engine – you set up smart systems that tirelessly work in the background, so your team can navigate growth with agility and confidence. We began by recognizing the daunting challenge of scale: more customers, more tasks, and the risk of overwhelm. But by methodically applying the steps in this guide – from identifying where automation can help, to implementing no-code tools, integrating AI, and continuously refining the process – you’ve seen how those challenges can transform into opportunities for efficiency and excellence.
Through Experience (mapping processes, building that first workflow) and Expertise (choosing the right tools, integrating AI effectively), you’ve empowered your startup to operate like a much larger company without the typical growing pains. We referenced industry insights and real examples to underscore that this isn’t just theory – businesses today are saving time, cutting costs, and improving customer satisfaction by embracing no-code and AI. By following suit, you’re not only keeping up with modern best practices; you’re positioning your startup at the forefront of a technological shift that levels the playing field for small teams. Non-technical founders can now implement systems that rival those of tech giants, thanks to these accessible tools.
Importantly, along this journey, we addressed the human element – assuring that your team is on board and that automation is augmenting their roles, not threatening them. The most successful scaling stories are ones where technology and people work hand-in-hand. Your team’s creativity and the relationships you build with customers remain crucial, and now they’re amplified by the fact that the “busy work” is largely handled by your automated helpers. This fosters a culture of innovation and proactiveness; instead of reacting to backlogs and errors, you’re strategizing for the next growth move or delighting a customer with personal attention.
As you look ahead, remember that scaling is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey. The no-code AI landscape is evolving rapidly – new tools, features, and possibilities will continue to emerge. The foundation you’ve built by following this guide gives you Authority and Trustworthiness in navigating that landscape. You can evaluate new opportunities (perhaps it’s an AI that can design UI, or a no-code tool that orchestrates entire business processes via voice commands – who knows!) and integrate them smoothly into your operations because you have a solid framework in place.
In closing, Scaling Your Startup with No-Code AI Automations isn’t just a catchy phrase – it’s a practical, powerful approach to growth. It’s about working smarter, not harder, and doing so in a way that is sustainable and even fun. Your startup can be lean yet mighty, using automations as force multipliers for every team member. By applying the step-by-step guide we’ve outlined, you’re investing in a future where your business can handle surges of demand, adapt quickly to change, and continually punch above its weight class. So here’s to your startup’s accelerated growth, fueled by no-code innovation and AI intelligence – may you reach new heights, one efficient step at a time!
Next Steps:
Translate this article – Would you like to read or share this guide in another language? We can quickly translate the entire article into Spanish, French, German, or any language of your choice for broader accessibility.
Generate blog-ready images – Enhance this article with custom blog images or infographics. We can create AI-generated images that align with each section (like a graphic of a robot assistant for automation, or a flowchart for the step-by-step guide) to make the content more visually engaging.
Start a new article – Have another topic in mind or a follow-up question? We can begin researching and crafting a new in-depth, SEO-optimized article. Whether it’s a deep dive into a specific no-code tool or another aspect of startup growth, let’s keep the momentum going and generate more insightful content for your needs.
